Kicking off with blockchain technology, this innovative system is changing the game in digital transactions. Imagine a secure, decentralized network where information is stored in blocks, linked together, and cryptographically secured. It’s like the coolest digital ledger ever created!
As we dive deeper, we’ll explore the various applications, inner workings, advantages, and potential pitfalls of this groundbreaking technology. Get ready to ride the wave of the future with blockchain!
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized system that enables the secure transfer of digital assets without the need for intermediaries like banks or payment processors. It consists of a chain of blocks containing transaction data, which are linked together using cryptographic principles to ensure transparency and immutability.
Decentralized Databases
In blockchain technology, decentralized databases are used to store transaction records across a network of computers, called nodes. Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain, and all transactions are verified and recorded in a transparent and secure manner. This decentralized approach eliminates the need for a central authority to control the data, making the system more resilient to cyber attacks and censorship.
Role of Cryptography
Cryptography plays a crucial role in blockchain technology by ensuring the security and integrity of transactions. Each block in the blockchain is secured using cryptographic hash functions, which create a unique fingerprint for the block. Additionally, digital signatures are used to authenticate transactions and verify the identity of participants. This encryption process makes it nearly impossible for malicious actors to alter transaction data or steal sensitive information.
Applications of Blockchain Technology

Blockchain technology has found applications across various industries, revolutionizing processes and enhancing security. Let’s delve into some examples of industries harnessing the power of blockchain technology.
Finance and Banking, Blockchain technology
- Blockchain technology has been widely adopted in the finance and banking sector to facilitate secure and transparent transactions.
- Smart contracts on blockchain platforms enable automated and efficient payment processing, reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum operate on blockchain technology, offering decentralized digital currencies.
Supply Chain Management
- Blockchain technology is transforming supply chain management by providing end-to-end visibility and traceability of products.
- Smart contracts help streamline processes like tracking inventory, verifying authenticity, and managing logistics.
- Companies can ensure the authenticity of products and reduce the risk of counterfeit goods through blockchain technology.
Healthcare Sector
- Blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize the healthcare sector by securely storing and sharing patient data.
- Medical records stored on blockchain platforms are immutable, ensuring data integrity and privacy.
- Healthcare providers can access real-time patient information securely, leading to improved care coordination and patient outcomes.
How Blockchain Works
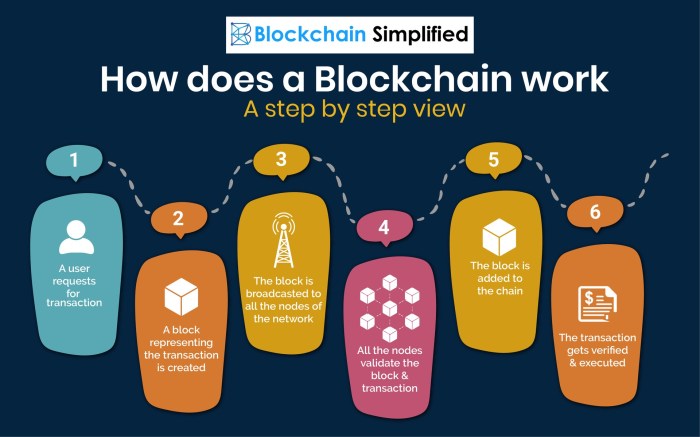
Blockchain technology operates through a decentralized network of nodes that work together to validate and record transactions. The process of adding a new block to the blockchain involves several key steps that ensure security and transparency.
Adding a New Block to the Blockchain
When a new transaction occurs, it is broadcasted to all nodes in the network. Each node collects these transactions into a block. To add a new block to the blockchain, the following steps are taken:
- Verification: Nodes in the network verify the validity of the transactions in the block.
- Consensus: Consensus mechanisms are used to agree on the order of transactions and validate the block.
- Hashing: The block is assigned a unique cryptographic hash that links it to the previous block.
- Adding to the Chain: Once the block is verified and hashed, it is added to the blockchain, creating a secure and immutable record of transactions.
Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain
Consensus mechanisms are protocols that ensure all nodes in the network agree on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain. Some common consensus mechanisms include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Requires nodes to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold, incentivizing them to act in the best interest of the network.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Selected nodes, known as delegates, validate transactions on behalf of the network.
Smart Contracts in Blockchain
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically enforce and execute the terms of the contract when predefined conditions are met. Smart contracts play a crucial role in blockchain technology by enabling trustless and secure transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers a range of benefits, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of using blockchain technology.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
- Decentralization: Blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority, giving more control to users.
- Transparency: All transactions on the blockchain are visible to all participants, enhancing trust and accountability.
- Security: The use of cryptographic algorithms makes it extremely difficult to alter data on the blockchain, ensuring data integrity.
- Immutability: Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted, providing a tamper-proof record.
- Efficiency: Transactions on the blockchain are processed quickly and without the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and delays.
Disadvantages of Blockchain Technology
- Scalability Issues: As the size of the blockchain grows, it can become slower and more resource-intensive to maintain.
- Energy Consumption: The process of mining and validating transactions on the blockchain requires a significant amount of energy.
- Lack of Regulation: The decentralized nature of blockchain can make it challenging to enforce regulations and resolve disputes.
- Privacy Concerns: While transactions are pseudonymous, they are still visible on the blockchain, raising privacy issues for some users.
- Complexity: Understanding and implementing blockchain technology can be complex and require specialized knowledge.