Investment strategy is the key to unlocking financial success in a dynamic market. Dive into the world of investing with this guide that delves into various strategies and techniques to help you make informed decisions and maximize your returns.
Introduction to Investment Strategy
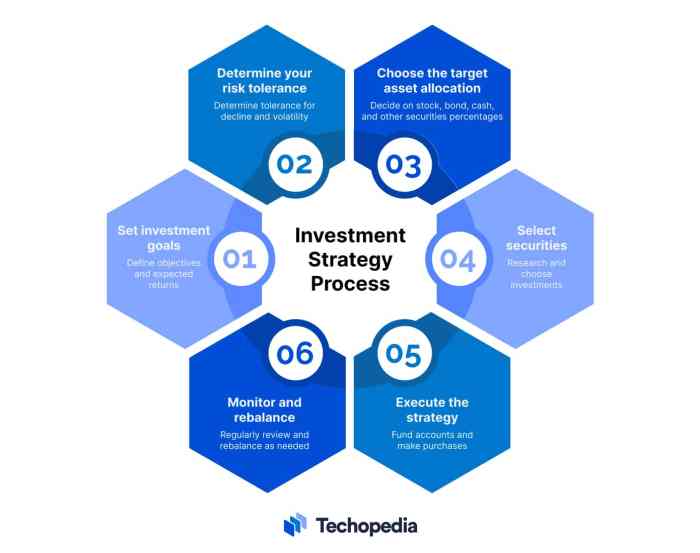
Investment strategy refers to a set plan or approach used by an individual or organization to allocate resources with the goal of achieving specific financial objectives. It involves making decisions on how to invest money in various financial instruments or assets to generate returns over time.
Importance of having a well-defined investment strategy
Having a well-defined investment strategy is crucial for several reasons:
- It helps individuals or organizations clearly Artikel their financial goals and objectives.
- It provides a roadmap for making informed investment decisions and managing risk.
- It helps in maintaining discipline and avoiding impulsive or emotional investment choices.
Common types of investment strategies
There are several common types of investment strategies that individuals or organizations can consider:
- Buy and Hold Strategy: This strategy involves buying assets and holding onto them for the long term, regardless of short-term market fluctuations.
- Value Investing: Investors following this strategy look for undervalued assets with the potential to increase in value over time.
- Growth Investing: This strategy focuses on investing in companies with strong growth potential, even if they may be overvalued in the short term.
- Income Investing: Investors using this strategy prioritize investments that generate regular income, such as dividends or interest payments.
Fundamental Analysis in Investment Strategy
Fundamental analysis is a method used by investors to evaluate the intrinsic value of a stock or security by analyzing various economic, financial, and qualitative factors that could affect its price in the future.
Examples of Fundamental Analysis Techniques
- Financial Statement Analysis: Examining a company’s balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement to assess its financial health and performance.
- Ratio Analysis: Calculating and comparing financial ratios like price-to-earnings ratio (P/E), earnings per share (EPS), and return on equity (ROE) to gauge a company’s profitability and efficiency.
- Valuation Models: Using techniques such as discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis or comparable company analysis to estimate the fair value of a stock.
How Fundamental Analysis Helps in Decision-making for Investment
Fundamental analysis provides investors with valuable insights into the overall health and potential growth of a company. By analyzing key financial metrics and industry trends, investors can make informed decisions about buying or selling stocks. Understanding the fundamental factors affecting a stock’s value can help investors identify undervalued or overvalued opportunities, leading to better investment outcomes.
Technical Analysis in Investment Strategy
Technical analysis plays a crucial role in investment strategy by analyzing past market data to predict future price movements. Unlike fundamental analysis, which focuses on company financials and economic indicators, technical analysis relies on charts and patterns to make investment decisions.
Common Technical Analysis Tools and Indicators
- Moving Averages: Used to identify trends by smoothing out price data over a specific period.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the speed and change of price movements to determine overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: Helps identify volatility and potential price breakouts by plotting standard deviations around a moving average.
- Candlestick Patterns: Visual representations of price movements that can indicate potential reversals or continuations.
Comparison of Fundamental and Technical Analysis
- Fundamental Analysis: Focuses on company financials, industry trends, and macroeconomic factors to determine the intrinsic value of a security.
- Technical Analysis: Relies on historical price data, volume, and chart patterns to forecast future price movements.
- Differences: While fundamental analysis looks at the value of a company, technical analysis is more concerned with price trends and market psychology. Investors often use a combination of both approaches to make well-rounded investment decisions.
Diversification in Investment Strategy

Diversification is a key concept in investment strategy, aimed at reducing risk by spreading investments across different asset classes.
Importance of Diversification
- Diversification helps to minimize the impact of a single investment underperforming or failing, as losses in one asset can be offset by gains in others.
- It can improve the overall risk-adjusted return of a portfolio by reducing volatility and enhancing stability.
Examples of Diversification in Action
- For instance, an investor who spreads their investments across stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities is less exposed to the risk of a downturn in a single market segment.
- By investing in both domestic and international markets, an investor can mitigate the risk of underperformance in a specific region.
Achieving Diversification in a Portfolio
- One way to achieve diversification is through asset allocation, where investments are spread across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, cash, and real estate.
- Investing in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) can also provide diversification as these funds hold a variety of securities within a single investment.
- Rebalancing a portfolio regularly can help maintain diversification by adjusting the allocation of assets based on market performance and changing economic conditions.
Risk Management in Investment Strategy
Investing in the financial markets comes with a certain level of risk that can impact the overall performance of a portfolio. Therefore, implementing effective risk management strategies is crucial to protect investments and maximize returns.
Significance of Risk Management
Effective risk management is essential in investment strategy as it helps investors mitigate potential losses and protect their capital. By identifying and assessing risks, investors can make informed decisions and adjust their portfolios accordingly to minimize negative impacts.
Different Risk Management Techniques
- Asset Allocation: Investors can diversify their portfolios by investing in a mix of different asset classes to reduce risk exposure.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Setting stop-loss orders can help investors limit their losses by automatically selling a security when it reaches a predetermined price.
- Hedging: Investors can use hedging strategies, such as options or futures contracts, to protect their portfolios from adverse market movements.
- Position Sizing: Proper position sizing ensures that investors do not allocate too much capital to a single investment, reducing the overall risk of the portfolio.
Impact of Risk Management Strategies
Effective risk management strategies can significantly impact investment decisions by providing investors with a sense of security and confidence in their portfolio. By actively managing risks and implementing appropriate techniques, investors can navigate volatile market conditions and achieve their financial goals.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Investment Strategies
When it comes to investing, one of the key decisions investors have to make is whether to adopt a long-term or short-term investment strategy. Each approach has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and understanding the differences between the two can help investors make informed decisions based on their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Long-Term Investment Strategy
Long-term investment strategies involve holding onto investments for an extended period, typically five years or more. This approach is often less focused on short-term market fluctuations and more on the overall growth potential of the investment. Some advantages of long-term investing include:
- Ability to ride out market volatility and take advantage of compound interest over time.
- Less emphasis on day-to-day market movements, reducing the stress of constantly monitoring investments.
- Potential for higher returns compared to short-term strategies, especially in the case of stocks and mutual funds.
It is important to note that long-term investing requires patience and a long-term perspective, as the value of investments may fluctuate over time.
Short-Term Investment Strategy
Short-term investment strategies involve buying and selling investments within a shorter time frame, often less than a year. This approach is more focused on taking advantage of short-term market trends and price movements. Some advantages of short-term investing include:
- Opportunity to capitalize on quick market gains and market inefficiencies.
- Flexibility to react to changing market conditions and economic events.
- Ability to generate income through active trading and market timing.
However, short-term investing comes with higher risks and transaction costs, as well as the potential for emotional decision-making based on short-term market fluctuations.
Overall, the choice between long-term and short-term investment strategies depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment time horizon. Long-term strategies are more suitable for investors looking for steady growth and willing to ride out market fluctuations, while short-term strategies may be suitable for investors seeking quick gains and willing to actively manage their investments.
Value Investing Strategy
Value investing is an investment approach that involves selecting stocks that are trading at a discount to their intrinsic value. The main principles of value investing include buying undervalued securities, focusing on long-term growth potential, and conducting thorough fundamental analysis.
Difference from Other Strategies, Investment strategy
Value investing differs from other strategies like growth investing or momentum investing in that it emphasizes the intrinsic value of a company rather than its potential for rapid growth or recent price trends. Value investors seek out companies that are trading below their true worth, based on factors like earnings, assets, and cash flow.
Notable Investors
- Warren Buffett: Known as one of the most successful value investors, Buffett’s investment approach is based on finding undervalued companies with strong fundamentals and holding them for the long term.
- Benjamin Graham: Considered the father of value investing, Graham’s book “The Intelligent Investor” laid the foundation for the principles of value investing.
- Seth Klarman: A renowned value investor and the author of “Margin of Safety,” Klarman is known for his disciplined approach to investing in undervalued securities.





